Purpose:
We investigated the efficacy of an innovative treatment in a small cohort of nine patients affected by mixed dry eye disease (MDED), i.e., both aqueous deficient and evaporative type. The treatment consists in the administration of a specific low-power, high-frequency electric current using the Rexon-Eye® device.
Methods:
Nine consecutive MDED patients were recruited and all treated. Therapy was administered with the Rexon-Eye® device (Resono Ophthalmic, Sandrigo, Italy, patented), which applies a low-power electric current with a specific spectrum of frequencies (4-64 MHz, Quantum Molecular Resonance, QMR®, patented). Patients were administered one 20 min treatment per week, for 4 weeks, and were examined at baseline and two month after the last treatment, by measuring: lipid layer thickness, tear meniscus, and non-invasive tear break-up time (NIBUT), all measured with IDRA (SBM Sistemi, Turin, Italy); Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) score; tear osmolarity (TearLab, Escondido (CA), USA); ocular inflammation (InflammaDry; Quidel, San Diego (CA), USA).
Results:
Results are reported in Table 1 and 2. The clinical endpoints improved significantly in most of the patients and no adverse events nor side effects were observed in any of them.
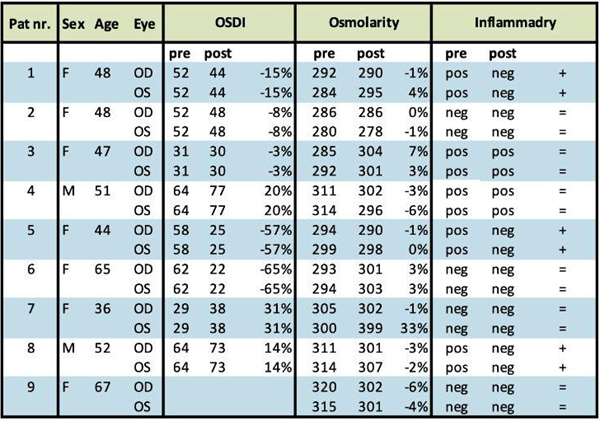
Table 1
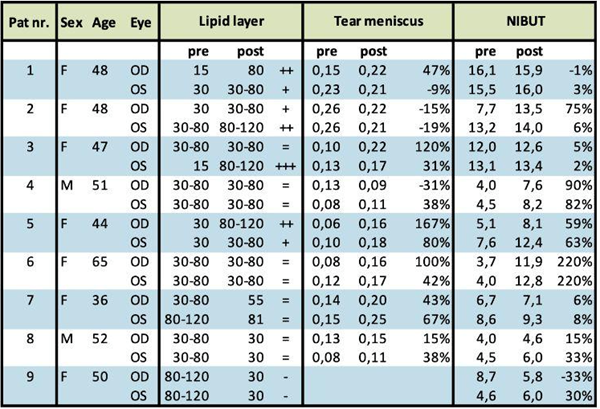
Table 2
Conclusions:
The innovative therapeutic device Rexon-Eye®, based on the QMR® patented electric stimulation, proved to be very effective in improving subjective and objective ocular parameters in most of the mixed dry eye patients of this study.