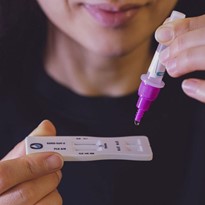
Rapid Antigen Tests: A Quick and Convenient Screening Tool
In the realm of infectious disease diagnosis, rapid antigen tests have emerged as a quick and convenient option for healthcare providers and patients alike. These tests are particularly relevant in the context of ongoing global health challenges, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, where timely diagnosis can significantly influence treatment and containment strategies.
This article discusses the advantages and limitations of rapid antigen tests, helping healthcare professionals make informed decisions about their use.
What Are Rapid Antigen Tests?
Rapid antigen tests are diagnostic tools designed to detect the presence of specific antigens related to infectious diseases, such as viruses or bacteria, within a patient's sample, typically collected from nasal swabs or saliva. Unlike traditional laboratory tests, which may require sophisticated equipment and longer processing times, rapid antigen tests provide results within minutes, allowing for immediate clinical decision-making.
Advantages of Rapid Antigen Tests
- Speed and Convenience: One of the most significant benefits of rapid antigen tests is their ability to deliver results in a short timeframe, often within 15 to 30 minutes. This rapid turnaround can be crucial in settings where timely diagnosis is essential, such as emergency rooms, clinics, and large-scale screening events.
- Ease of Use: Many rapid antigen tests are user-friendly and do not require specialized training or equipment, making them accessible for a wide range of healthcare providers. This ease of use allows for point-of-care testing, enabling immediate assessment and management of patients.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to more complex diagnostic tests, rapid antigen tests are often less expensive, making them an attractive option for healthcare facilities, particularly in resource-limited settings. This affordability can facilitate widespread testing, helping to identify cases and reduce transmission rates.
- Facilitating Public Health Responses: The rapid nature of these tests can support public health initiatives, enabling quick identification of positive cases and facilitating prompt isolation or treatment. This is particularly important during outbreaks, where controlling the spread of infection is critical.
- Testing in Diverse Settings: Rapid antigen tests can be performed in various environments, including clinics, schools, workplaces, and at home. This flexibility increases testing accessibility and allows for broader screening efforts.
Limitations of Rapid Antigen Tests
- Sensitivity and Specificity: Rapid antigen tests generally exhibit lower sensitivity compared to PCR (polymerase chain reaction) tests. This means they have a higher likelihood of producing false negative results, particularly in asymptomatic individuals or those with low viral loads. For accurate diagnosis, it is essential to consider confirmatory testing, especially in high-risk populations.
- Timing of Testing: The accuracy of rapid antigen tests is influenced by the stage of infection. These tests are less likely to detect the virus in the early stages of infection, where viral loads may be low, or after symptoms have resolved, when the presence of antigens may diminish. Testing at the right time is crucial for reliable results.
- Variability in Test Quality: While the accuracy and reliability of rapid antigen tests can vary among different manufacturers, healthcare providers should select tests that have been validated by relevant regulatory bodies. For instance, in the United States and Australia, tests may receive provisional or Emergency Use Authorisation (EUA) from the FDA or TGA respectively, while other countries may have their specific approval processes.
- Need for Confirmation: Due to their lower sensitivity, positive results from rapid antigen tests may require confirmation through more sensitive methods, such as PCR tests, especially in high-risk populations or clinical settings. This need for follow-up testing can complicate the testing process and potentially delay diagnosis and treatment.
- Interpretation of Results: The interpretation of rapid antigen test results requires careful consideration of clinical symptoms and epidemiological context. False positives can occur, especially in low-prevalence settings, leading to unnecessary isolation or further testing.
Conclusion
Rapid antigen tests represent a valuable tool in the diagnostic arsenal for infectious diseases, offering speed, convenience, and cost-effectiveness. However, their limitations, particularly regarding sensitivity and the need for confirmatory testing, must be carefully considered when implementing them in clinical practice. By understanding both the advantages and limitations of rapid antigen tests, healthcare providers can make informed decisions that enhance patient care and contribute to effective public health responses.



























-205x205.jpg)


-205x205.jpg)