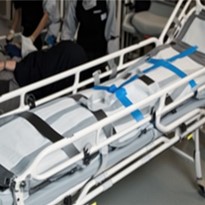
In the realm of emergency response and medical care, the rescue stretcher stands as an indispensable tool. When lives hang in the balance, it is the stretcher that bridges the gap between the site of an incident and the sanctuary of medical attention. Whether in the chaotic aftermath of an accident, the tight corridors of a healthcare facility, or the remote wilderness, rescue stretchers are relied upon to safely transport injured individuals. Yet, their effectiveness hinges not just on their initial quality but also on the rigorous maintenance and inspection routines they undergo.
I. Establishing Regular Inspection and Maintenance Schedules
A. The Significance of Having a Structured Inspection and Maintenance Plan
- Ensuring Reliability During Critical Moments: In the world of emergency response, reliability is paramount. A rescue stretcher malfunction during a critical operation can lead to dire consequences. A structured inspection and maintenance plan serve as the bulwark against unforeseen failures, instilling confidence in first responders and healthcare providers alike.
- Compliance with Safety Standards and Regulations: In the realm of healthcare and emergency services, regulatory compliance is non-negotiable. Adhering to safety standards and regulations is not just a matter of bureaucratic necessity; it is a commitment to safeguarding lives. A well-structured maintenance plan ensures compliance, reducing legal and ethical risks.
B. Determining Frequency and Intervals for Inspections and Maintenance
- Daily, Weekly, Monthly, and Annual Checks: Rescue stretchers, due to their intensive use, require a tiered approach to inspections and maintenance. Daily checks focus on immediate safety concerns and functionality, while weekly, monthly, and annual checks delve into deeper levels of assessment. This tiered approach helps in balancing the need for regular scrutiny without disrupting operational efficiency.
C. Documentation and Record-keeping for Tracking Maintenance History
- Benefits of Maintaining Detailed Records: Behind every well-maintained rescue stretcher lies a meticulous trail of records. These records are not mere paperwork; they are the chronicle of a stretcher's journey from its first use to its most recent inspection. Detailed records facilitate accountability, track trends in wear and tear, and provide an invaluable resource for making informed decisions.
- Recommended Data to Include in Records: Effective record-keeping encompasses essential details such as inspection dates, maintenance performed, replacement parts, and the names of responsible personnel. A well-documented history simplifies audits, aids in warranty claims, and serves as a foundation for continuous improvement.
II. Cleaning and Disinfection Practices for Infection Control
A. Importance of Infection Control in Rescue Stretcher Maintenance
- Infection control is a paramount concern when it comes to maintaining rescue stretchers, as these devices are frequently exposed to various environments and situations.
- Ensuring infection control helps safeguard both patients and healthcare providers, reducing the risk of cross-contamination.
- Proper cleaning and disinfection practices are essential not only for hygiene but also for maintaining the integrity of stretcher materials.
B. Cleaning Procedures for Different Stretcher Materials (Metal, Plastic, Fabric)
Different stretcher materials require specific cleaning approaches to prevent damage or deterioration:
- Metal Stretcher Frames:
- Use a non-abrasive, pH-neutral cleaner to prevent corrosion.
- Pay special attention to joints and hinges.
- Rinse thoroughly and dry to prevent water stains.
- Plastic Stretcher Components:
- Wipe down with a mild detergent and water solution.
- Avoid abrasive scouring pads to prevent scratching.
- Ensure thorough rinsing to remove detergent residues.
- Fabric Stretcher Surfaces:
- Vacuum regularly to remove debris.
- Spot clean stains with a fabric-specific cleaner.
- Follow manufacturer recommendations for deep cleaning or machine washing if applicable.
C. Selection of Appropriate Disinfectants and Their Safe Application
The choice of disinfectant is critical to ensure effective disinfection without harming stretcher materials:
- Alcohol-Based Disinfectants:
- Suitable for metal components.
- Rapid drying and effective against many pathogens.
- Avoid prolonged contact with plastics, as it may cause degradation.
- Quaternary Ammonium Compounds (Quats):
- Safe for a wide range of materials, including plastics.
- Read labels to ensure compatibility with stretcher materials.
- Follow recommended contact times for effective disinfection.
- Hydrogen Peroxide-Based Disinfectants:
- Generally safe for most stretcher materials.
- Check compatibility with specific materials.
- May require rinsing to remove residues.
D. Best Practices for Handling Biohazardous Materials and Contaminants
When dealing with biohazardous materials or contaminants, additional precautions are essential:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Ensure that all personnel involved wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, gowns, and masks.
- Use eye protection if there is a risk of splashing.
- Containment and Disposal:
- Contain biohazardous materials securely in leak-proof bags or containers.
- Follow established protocols for disposal in compliance with local regulations.
- Decontamination Protocols:
- Stretcher components exposed to biohazardous materials should undergo thorough decontamination.
- Follow strict decontamination procedures to minimize the risk of infection transmission.
III. Assessing Wear and Tear: Wheels, Straps, and Frame
Assessing the condition of your rescue stretcher is a fundamental aspect of its maintenance. Regularly inspecting for wear and tear ensures that your stretcher remains reliable during critical moments. This section outlines the inspection techniques, common areas prone to wear and tear, and guidelines for assessing damage severity.
A. Inspection Techniques for Identifying Wear and Tear
- Visual Inspection
- Conduct a thorough visual examination of the entire stretcher surface.
- Look for signs of physical damage such as cracks, dents, or scratches
- Pay special attention to any areas with visible wear or discoloration.
- Check for loose or missing components, fasteners, and screws.
- Inspect labels and safety information for clarity and legibility.
- Functional Testing
- Test the stretcher's functionality according to manufacturer guidelines.
- Ensure that all moving parts, such as folding mechanisms or height adjustment mechanisms, operate smoothly and securely.
- Verify that safety features like locking mechanisms are functioning correctly.
- Test the mobility of wheels and axles, making sure they rotate freely without wobbling.
B. Common Areas Prone to Wear and Tear
- Wheels and Axles
- Wheels and axles are critical components that frequently experience wear.
- Inspect wheels for uneven wear patterns or flat spots.
- Check axles for signs of bending or corrosion.
- Ensure that wheel locks engage and release properly.
- Straps and Harnesses
- Examine straps and harnesses for fraying, tears, or signs of stretching.
- Test the strength and integrity of attachment points and buckles.
- Replace any damaged or weakened straps promptly to maintain patient safety.
- Frame Integrity
- Scrutinize the frame structure for cracks, deformation, or weakened joints.
- Verify that the frame is stable and free from structural issues.
- Pay attention to areas where the frame may have been stressed during use.
C. Guidelines for Assessing Damage Severity and Determining Repair or Replacement
- When assessing damage, consider factors such as the extent of wear, the criticality of the affected component, and the manufacturer's recommendations.
- Classify damage into categories such as minor, moderate, or severe to prioritize repairs.
- Minor damage may require simple fixes, while moderate or severe damage might necessitate component replacement or professional repair services.
- Always adhere to safety and compatibility standards when making repairs or replacements.
IV. Replacing Components and Upholding Stretcher Functionality
Understanding the role of spare parts and components is essential to maintaining your rescue stretcher's functionality. This section provides guidance on sourcing high-quality replacement parts, using proper tools and techniques for component replacement, and ensuring that replacements meet safety and compatibility standards.
A. Understanding the Role of Spare Parts and Components
- Spare parts are integral to keeping your stretcher in optimal working condition.
- Components like wheels, straps, frames, and fasteners may require replacement over time.
- Familiarize yourself with the manufacturer's documentation to identify compatible replacement parts.
B. Sourcing High-Quality Replacement Parts
- Purchase replacement parts from reputable suppliers or directly from the manufacturer.
- Ensure that replacement components meet safety standards and specifications outlined by the manufacturer.
- Verify the authenticity of parts to prevent counterfeit or substandard replacements.
C. Proper Tools and Techniques for Component Replacement
- Use the appropriate tools recommended by the manufacturer for component replacement.
- Follow step-by-step instructions provided in the manufacturer's maintenance manual.
- Exercise caution and precision to avoid damaging the stretcher during the replacement process.
D. Ensuring That Replacements Meet Safety and Compatibility Standards
- Prioritize safety and compliance with manufacturer specifications when installing replacement parts.
- Verify that the replaced components function correctly and securely.
- Conduct functional testing after replacement to confirm that the stretcher operates as intended.
V. Prolonging the Lifespan of Rescue Stretchers Through Careful Maintenance
Rescue stretchers are indispensable tools in emergency response scenarios, and their reliability is paramount. Regular maintenance plays a pivotal role in ensuring that these life-saving devices perform optimally when they are needed most. In this section, we will delve into the long-term benefits of systematic maintenance, offer valuable tips for proper storage and handling, emphasize the importance of training for stretcher operators and maintenance personnel, and conclude with a reminder of the shared responsibility we all hold in maintaining rescue stretchers in peak condition.
A. The Long-Term Benefits of Regular Maintenance
- Enhanced Reliability: Routine maintenance significantly increases the reliability of rescue stretchers. When every component is inspected, cleaned, and serviced as needed, the risk of unexpected malfunctions during critical missions is substantially reduced.
- Cost Savings: While maintenance incurs some expenses, it pales in comparison to the cost of replacing an entire stretcher or dealing with the consequences of a malfunction during an emergency. Regular upkeep ultimately saves resources in the long run.
- Extended Lifespan: Proper maintenance can extend the operational lifespan of rescue stretchers. By addressing wear and tear promptly, you can maximize the utility of your stretchers for years to come.
B. Tips for Storage and Handling to Prevent Damage
- Proper Storage: Store stretchers in a clean, dry, and climate-controlled environment. Avoid exposing them to extreme temperatures, direct sunlight, or moisture, as these factors can degrade materials over time.
- Adequate Space: Ensure there is sufficient space to maneuver and handle stretchers without the risk of collisions or damage. Implementing designated storage areas or racks can help prevent accidents.
- Secure Fastening: When not in use, secure all straps, harnesses, and attachments to prevent tangling and potential damage. Keep stretchers in their designated storage positions.
C. Training and Education for Stretcher Operators and Maintenance Personnel
- Operator Training: Provide comprehensive training to stretcher operators on proper handling, loading, and securing techniques. Ensure they understand the limitations and weight capacities of the stretchers.
- Maintenance Training: Maintenance personnel should receive specialized training in stretcher maintenance and repair. This includes recognizing signs of wear, following maintenance schedules, and safely replacing components.
Final Thoughts on the Responsibility of Maintaining Rescue Stretchers in Optimal Condition
The responsibility of maintaining rescue stretchers doesn't rest solely on the shoulders of a few individuals; it's a collective duty. Every person involved in emergency response, from operators to administrators, plays a crucial role in ensuring that these life-supporting devices are always ready for action. By adhering to structured maintenance plans, implementing proper storage practices, and investing in training, we can collectively uphold the reliability and effectiveness of rescue stretchers, ultimately contributing to better outcomes in critical situations.