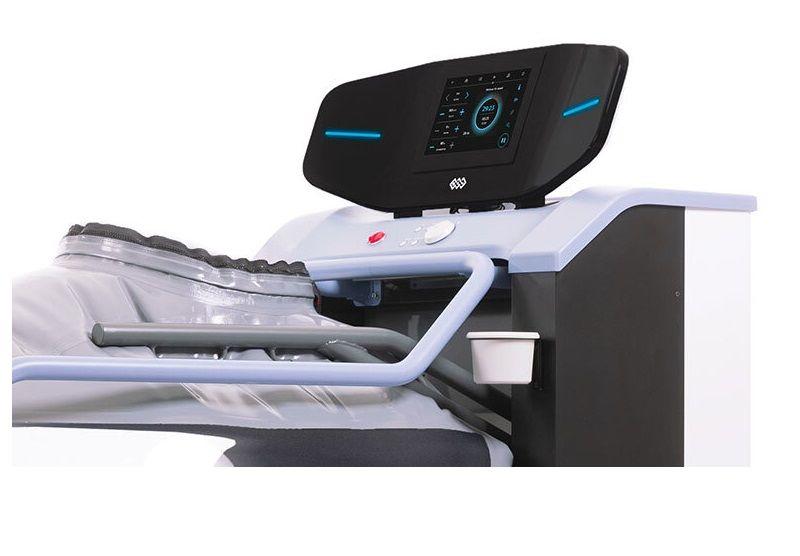
As neurological conditions are considered the leading cause of disability and the second leading cause of death worldwide, it is necessary to respond to their increased burden by introducing new medical technologies enabling safe, effective and time-saving rehabilitation.
A total of 39 neurological patients completed a treatment program involving six body-weight supported treadmill exercise sessions combined with conventional rehabilitation. The evolution of the symmetry index for the parameters stance time, step length, step time, swing time, swing/stance time ratio and weight-bearing proportion was evaluated.
The asymmetry of all monitored gait parameters improved statistically significantly within the entire cohort of treated patients by 40%, 50%, 61%, 62%, 68% and 67% in terms of stance time, step length, step time, swing time, swing/stance time ratio and weight loading proportion, respectively. The comparison of the indication groups shows that post-stroke patients achieved the highest average improvement across all gait parameters.